Repair of switching power supply
Video cameras, like cars, have now ceased to be luxury items and have become necessary devices. But, if the video camera itself is made with high quality and its failure without any external reasons is an infrequent phenomenon, then with the power supplies for them everything is just the opposite - they “burn” with enviable consistency. And if we buy chargers from cell phones without thinking, then purchasing a power supply for the required voltage and current can cause some problems.
However, a failed switching power supply can often be restored independently.

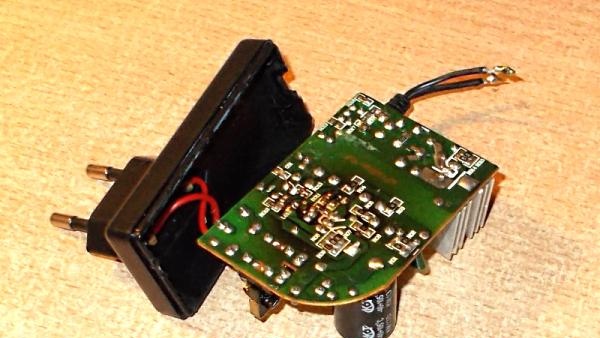
The photo shows a faulty switching power supply, model FC-2000. The output voltage of the power supply is 12 volts with a load of up to 2 A, which is quite enough to power one or two video cameras. After two and a half years of operation around the clock, the voltage at its output disappeared completely.

Having opened the case of a faulty power supply, we will find a board with parts installed on it - among them an electrolytic capacitor with a capacity of 10 to 47-68 μF and with an operating voltage of 400-450 volts; Even after a few minutes, a fairly large charge remains on its terminals.Therefore, first of all, you need to short-circuit its terminals through a resistance with a nominal value of several kOhms and a power above 0.5 W. You cannot directly short-circuit the terminals of the capacitor, as this may damage it. In the photo in the red rectangle is exactly this detail. Since the bottom of the capacitor is swollen, we can say that the first fault has been detected.

In addition to the above-mentioned mains rectifier filter capacitor, parts such as a fuse, a rectifier bridge (either a rectifier unit or four separate diodes can be installed, as in the photo) and a transistor switch are also subject to inspection - in the photo they are enclosed in green rectangles.

The operating voltage of the new capacitor must not be lower than that for which the replacement one was designed. For testing, you can get by with a smaller capacitance, but to ensure normal operation of the power supply, this parameter must be either the same or higher by one position (i.e., a capacitance of 33 μF can be increased to 47 μF).

Since in the described case the parts of the high-voltage rectifier and the transistor turned out to be serviceable, we apply mains voltage to its input. If you had to change diodes or a transistor, the first switching on of the power supply should be done through a 25-40 W incandescent lamp connected in series - thanks to this, in the presence of hidden faults, the amount of current flowing through the primary power supply circuits will not be fatal.
We connect a voltmeter to the terminals - the voltage is within normal limits. However, having connected even a small load, the output voltage began to change abruptly from 5 to 11 volts, which indicates a malfunction of the stabilization circuits.

Further inspection revealed a malfunction of another electrolytic capacitor installed in the PC 817 optocoupler circuit.

Judging by the photo, the capacitor has lost about 90% of its capacity.
After installing new parts, carefully wash off any remaining flux (rosin, solder paste, etc.) with acetone or alcohol to avoid current leaks and possible breakdown and burnout of the board material.

Check the power supply again. This time, a car lamp with a power of 21 W and a current consumption of about 2 amperes is connected to its terminals - the power supply is designed for exactly this rated operating current. As you can see in the photo, he coped with his task “excellently”, the light is bright, and he also managed to save 200-300 rubles and the time that would have been spent searching for a new switching power supply.
However, a failed switching power supply can often be restored independently.

The photo shows a faulty switching power supply, model FC-2000. The output voltage of the power supply is 12 volts with a load of up to 2 A, which is quite enough to power one or two video cameras. After two and a half years of operation around the clock, the voltage at its output disappeared completely.

Having opened the case of a faulty power supply, we will find a board with parts installed on it - among them an electrolytic capacitor with a capacity of 10 to 47-68 μF and with an operating voltage of 400-450 volts; Even after a few minutes, a fairly large charge remains on its terminals.Therefore, first of all, you need to short-circuit its terminals through a resistance with a nominal value of several kOhms and a power above 0.5 W. You cannot directly short-circuit the terminals of the capacitor, as this may damage it. In the photo in the red rectangle is exactly this detail. Since the bottom of the capacitor is swollen, we can say that the first fault has been detected.

In addition to the above-mentioned mains rectifier filter capacitor, parts such as a fuse, a rectifier bridge (either a rectifier unit or four separate diodes can be installed, as in the photo) and a transistor switch are also subject to inspection - in the photo they are enclosed in green rectangles.

The operating voltage of the new capacitor must not be lower than that for which the replacement one was designed. For testing, you can get by with a smaller capacitance, but to ensure normal operation of the power supply, this parameter must be either the same or higher by one position (i.e., a capacitance of 33 μF can be increased to 47 μF).

Since in the described case the parts of the high-voltage rectifier and the transistor turned out to be serviceable, we apply mains voltage to its input. If you had to change diodes or a transistor, the first switching on of the power supply should be done through a 25-40 W incandescent lamp connected in series - thanks to this, in the presence of hidden faults, the amount of current flowing through the primary power supply circuits will not be fatal.
We connect a voltmeter to the terminals - the voltage is within normal limits. However, having connected even a small load, the output voltage began to change abruptly from 5 to 11 volts, which indicates a malfunction of the stabilization circuits.

Further inspection revealed a malfunction of another electrolytic capacitor installed in the PC 817 optocoupler circuit.

Judging by the photo, the capacitor has lost about 90% of its capacity.

After installing new parts, carefully wash off any remaining flux (rosin, solder paste, etc.) with acetone or alcohol to avoid current leaks and possible breakdown and burnout of the board material.

Check the power supply again. This time, a car lamp with a power of 21 W and a current consumption of about 2 amperes is connected to its terminals - the power supply is designed for exactly this rated operating current. As you can see in the photo, he coped with his task “excellently”, the light is bright, and he also managed to save 200-300 rubles and the time that would have been spent searching for a new switching power supply.
Similar master classes
Particularly interesting
Comments (4)












