Electronic desulfator
Anyone who has ever asked the question "Why does the battery fail?", knows that most batteries fail precisely due to sulfation of the plates. All lead-acid batteries are susceptible to this phenomenon.

I was surprised by how easy it is to recondition a battery with an electronic desulfator. In fact, all the manipulations boiled down to connecting the miracle device to the battery and the restoration of the sulfated plates would begin. Moreover, there was no need to even remove the battery from the car, unscrew the caps of the cans to remove excess gas, and perform any other actions. You don't even need to connect a charger. And you practically don’t need any special control - just throw on the terminals and go do your thing, and the device will do everything itself.
Thanks to the device in question, you can not only restore your battery, but also carry out preventive maintenance on batteries that are still in service. This way you will extend their service life for years.
The desulfator is powered by a battery, which it regenerates.Using the same power circuit, it generates reverse short powerful high-frequency pulses. It has long been known that such pulses bring lead sulfate molecules into resonance, as a result of which the reverse process occurs - desulfation and the battery restores its capacity and resistance.
Of course, this restoration method also has disadvantages: not all batteries can be restored, but about 85 percent. And this, I tell you, is a very good chance to try this method. Another disadvantage is the very long recovery process, which can last from a day to a month.
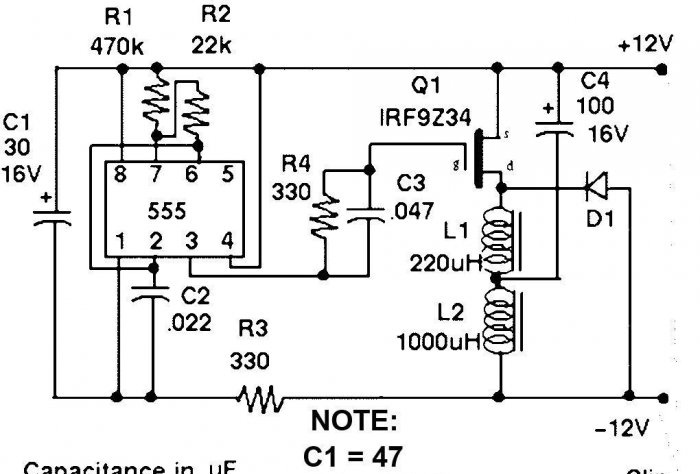
The 555 chip contains a master oscillator, which generates short pulses with a frequency of 1-3 kHz. Elements C1 and R3 filter the voltage, ensuring normal operation of the generator. The output of the microcircuit is loaded onto a transistor, which switches the inductance. It is in coil L1 that a powerful short pulse occurs after the transistor closes. This pulse is returned back to the battery through diode D1 and capacitor C4.
Details:
C1, C4 – capacity is indicated in microfarads. It is better to take C1 not at 30 µF, but at 300 µF. It is better to make C4 composite by connecting 4 22 μF capacitors in parallel, since a very large load is placed on it.
Inductors L1 and L2 are wound on ferrite rings. It all depends on the permeability of the magnetic core and the diameter of the ring. L1 contains approximately 45 turns of 0.8 mm wire, and coil L2 contains 70 turns of such wire. In general, I recommend using a tester that measures inductance when winding coils. Rings can be taken from unnecessary computer power supplies.
D1 – any powerful 15-25 A.
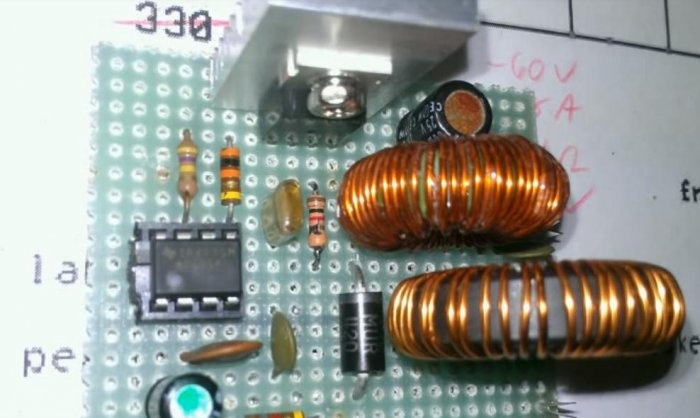
I assembled the circuit on a breadboard and soldered the jumpers from below with pieces of wire. The transistor was installed on a small heat sink.
Then I installed this board in a homemade case. Of course, the dimensions are too high and the device could be made much more compact.
It is advisable to connect the desulfator to the battery through a fuse, about two amperes. Although the strength of the impulses there is much greater, their duration is not enough to damage the fuse.
After connecting the device, you should hear a faint squeak indicating normal operation of the device.
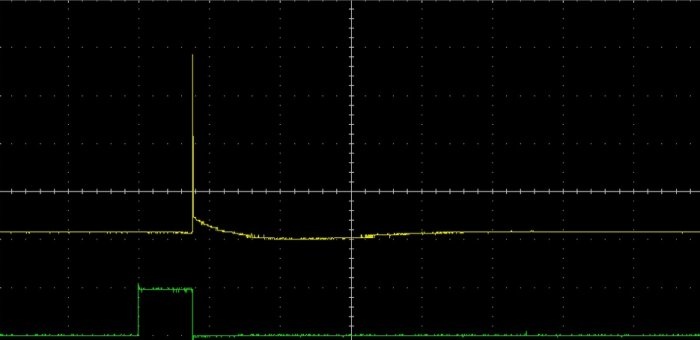
Well, the final check can only be done using an oscilloscope. To do this, first connect the probes to the input of the transistor (green diagram). After making sure that the generator is working, you can connect the probes parallel to the output of the device (yellow diagram). And you will see periodic peak-shaped pulses indicating normal operation of the desulfator. At their peak, these pulses reach 30 V, and at the terminals of the battery itself. And the current strength fluctuates in the range of 15-25 A.
Before restoring, it is advisable to fully charge the battery. If you are going to restore a battery standing on a car, then be sure to disconnect one power terminal of the car so as not to damage the electronics of your car.
Next, connect the desulfator and wait. The waiting time is always individual. All you need to do is periodically monitor the battery - measure the voltage to prevent complete discharge. Voltage measurements must be made with the desulfator turned off, this is mandatory.
The maximum result can be obtained only after 4 weeks of continuous operation of the desulfator.
Although the device is autonomous, I do not recommend leaving it unattended.
Ali Express you can buy a ready-made kit for assembly, see - HERE.
Or a completely finished device, see - HERE.

I was surprised by how easy it is to recondition a battery with an electronic desulfator. In fact, all the manipulations boiled down to connecting the miracle device to the battery and the restoration of the sulfated plates would begin. Moreover, there was no need to even remove the battery from the car, unscrew the caps of the cans to remove excess gas, and perform any other actions. You don't even need to connect a charger. And you practically don’t need any special control - just throw on the terminals and go do your thing, and the device will do everything itself.
Thanks to the device in question, you can not only restore your battery, but also carry out preventive maintenance on batteries that are still in service. This way you will extend their service life for years.
How the desulfator works
The desulfator is powered by a battery, which it regenerates.Using the same power circuit, it generates reverse short powerful high-frequency pulses. It has long been known that such pulses bring lead sulfate molecules into resonance, as a result of which the reverse process occurs - desulfation and the battery restores its capacity and resistance.
Of course, this restoration method also has disadvantages: not all batteries can be restored, but about 85 percent. And this, I tell you, is a very good chance to try this method. Another disadvantage is the very long recovery process, which can last from a day to a month.
Desulfator circuit
The 555 chip contains a master oscillator, which generates short pulses with a frequency of 1-3 kHz. Elements C1 and R3 filter the voltage, ensuring normal operation of the generator. The output of the microcircuit is loaded onto a transistor, which switches the inductance. It is in coil L1 that a powerful short pulse occurs after the transistor closes. This pulse is returned back to the battery through diode D1 and capacitor C4.
Details:
C1, C4 – capacity is indicated in microfarads. It is better to take C1 not at 30 µF, but at 300 µF. It is better to make C4 composite by connecting 4 22 μF capacitors in parallel, since a very large load is placed on it.
Inductors L1 and L2 are wound on ferrite rings. It all depends on the permeability of the magnetic core and the diameter of the ring. L1 contains approximately 45 turns of 0.8 mm wire, and coil L2 contains 70 turns of such wire. In general, I recommend using a tester that measures inductance when winding coils. Rings can be taken from unnecessary computer power supplies.
D1 – any powerful 15-25 A.
Desulfator assembly
I assembled the circuit on a breadboard and soldered the jumpers from below with pieces of wire. The transistor was installed on a small heat sink.
Then I installed this board in a homemade case. Of course, the dimensions are too high and the device could be made much more compact.
Checking the operation of the desulfator
It is advisable to connect the desulfator to the battery through a fuse, about two amperes. Although the strength of the impulses there is much greater, their duration is not enough to damage the fuse.
After connecting the device, you should hear a faint squeak indicating normal operation of the device.
Well, the final check can only be done using an oscilloscope. To do this, first connect the probes to the input of the transistor (green diagram). After making sure that the generator is working, you can connect the probes parallel to the output of the device (yellow diagram). And you will see periodic peak-shaped pulses indicating normal operation of the desulfator. At their peak, these pulses reach 30 V, and at the terminals of the battery itself. And the current strength fluctuates in the range of 15-25 A.
Battery recovery process
Before restoring, it is advisable to fully charge the battery. If you are going to restore a battery standing on a car, then be sure to disconnect one power terminal of the car so as not to damage the electronics of your car.
Next, connect the desulfator and wait. The waiting time is always individual. All you need to do is periodically monitor the battery - measure the voltage to prevent complete discharge. Voltage measurements must be made with the desulfator turned off, this is mandatory.
The maximum result can be obtained only after 4 weeks of continuous operation of the desulfator.
Although the device is autonomous, I do not recommend leaving it unattended.
Chinese desulfator
Ali Express you can buy a ready-made kit for assembly, see - HERE.
Or a completely finished device, see - HERE.
Watch the video on assembling the Chinese kit
See video on how to restore a battery using a desulfator
Similar master classes
Particularly interesting
Comments (6)