How to make a digital microscope from a web camera
It's no secret that the world around us has subtle structures, the organization and structure of which cannot be discerned by the human eye. The entire universe remained inaccessible and unknown until the microscope was invented.
We all know this device from school. In it we looked at bacteria, living and dead cells, objects and objects that we all see every day. Through a narrow viewing lens, they miraculously turned into models of lattices and membranes, nerve plexuses and blood vessels. At such moments you realize how big and multifaceted this world is.
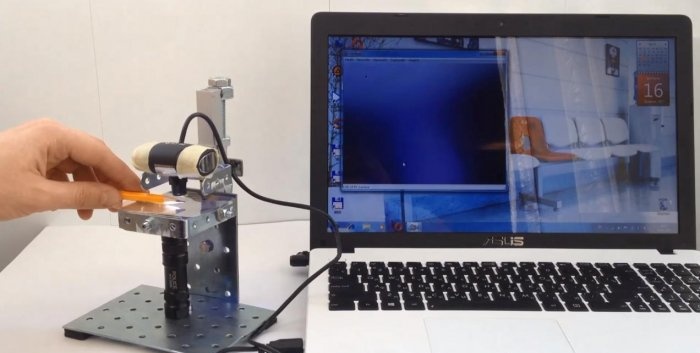
Recently, microscopes have begun to be made digital. They are much more convenient and efficient, because now you don’t have to look closely at the lens. Just look at the monitor screen, and we see an enlarged digital image of the object in question. Imagine that you can make such a miracle of technology with your own hands from an ordinary webcam. Don't believe me? We invite you to verify this with us.
Materials:
Tools:
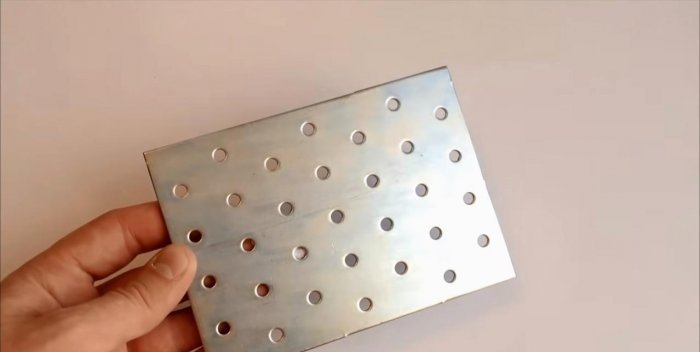
For the tripod base of the microscope we use perforated plates and metal corners. They are used to join wooden products. They are easily bolted together, and many holes allow this to be done at the required level.
We cover the flat perforated plate on the back side with soft furniture pads. We simply glue them on the corners of the rectangle.
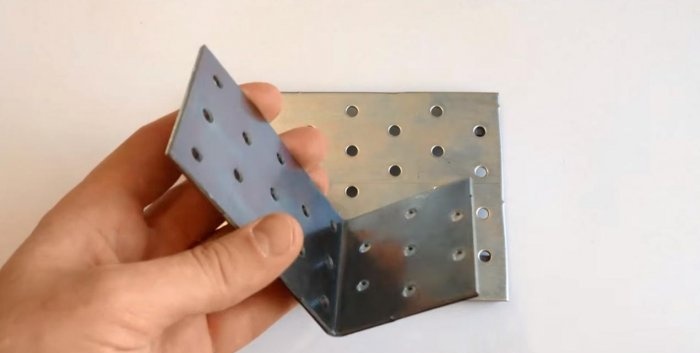
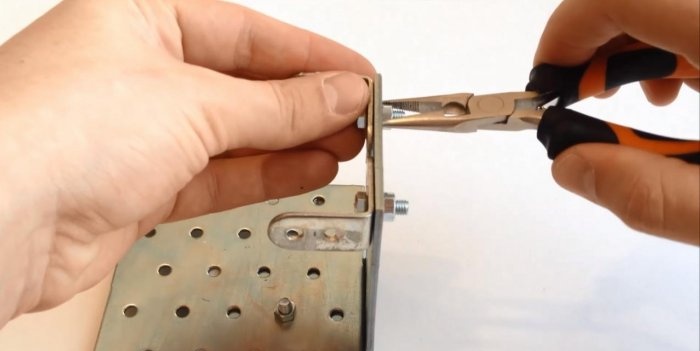
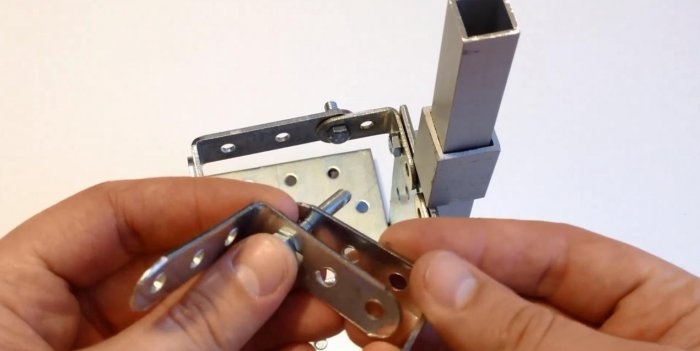
The next element will be a bracket or corner with versatile shelves. We fasten the short shelf of the bracket and the base plate with a bolt and nut. We tighten them with pliers for reliability.
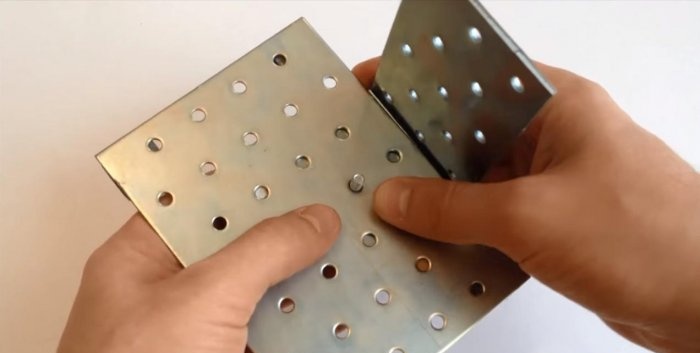
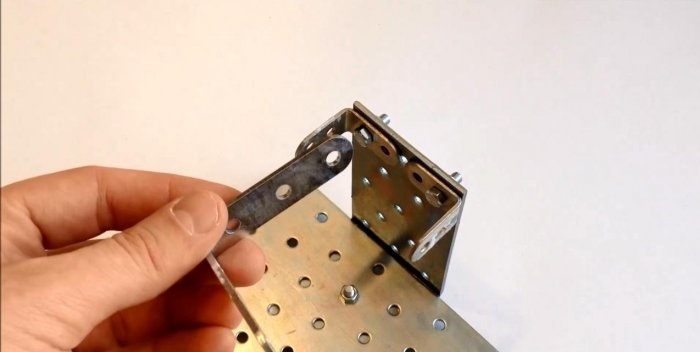
We mount two small brackets on the edge of the plate on both sides. We attach two more longer corners to them so that we form a small frame. This will be the base for the microscope viewing glass. It can be made from a small piece of thin glass.
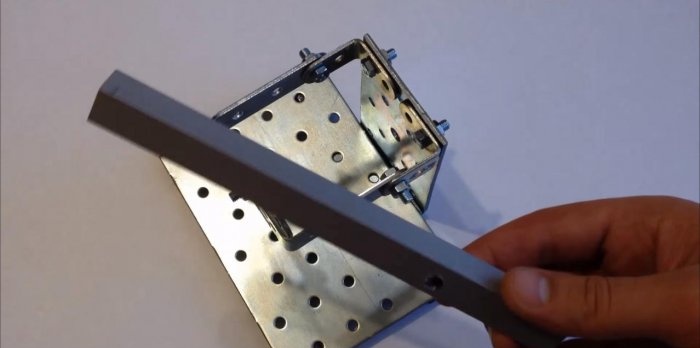
We make a tripod from a piece of square profile pipe 15x15 mm. Its height should be about 200-250 mm. There is no point in doing more, since exceeding the distance from the viewing glass reduces the quality of the image, and less risks being overexposed and incorrect.
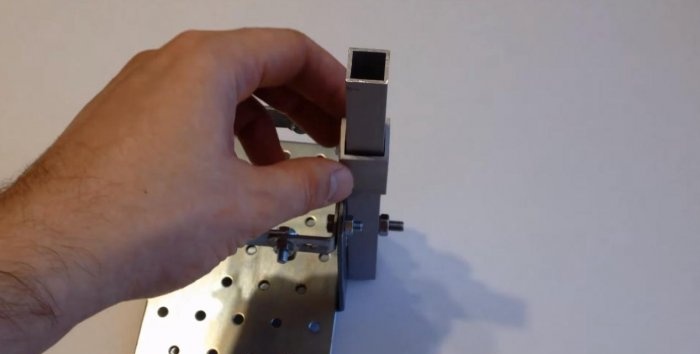
We attach the tripod to a perforated bracket, and on top of it we place a small piece of 20x20 pipe so that it moves freely along this stand.
We make an open frame from two brackets overlapped with each other. We choose longer bolts so that they are enough to tighten this frame around the moving section of the pipe. We place a plate with two holes on the sides on them and secure it with nuts.
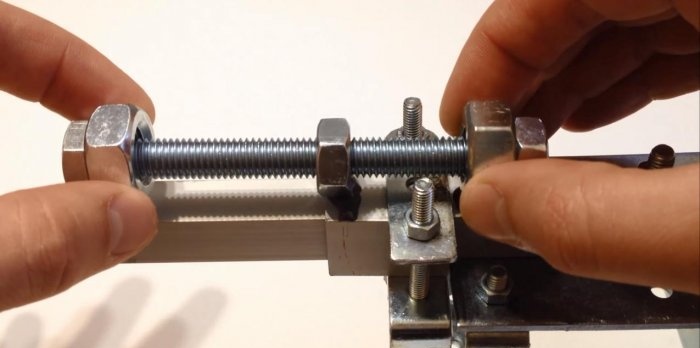
To adjust the distance of the frame from the viewing glass, use an M8x100 mm bolt. We will need two nuts to fit the bolt size, and two larger ones. We take epoxy glue and glue the bolt nuts to the tripod in three places. A nut screwed onto the end of a bolt can also be secured with epoxy.
In place of the tube with an eyepiece in our microscope there will be a regular webcam. The higher the resolution, the better; the connection to a computer can be either wired (USB 2.0, 3.0), or via Wi Fi or Bluetooth.
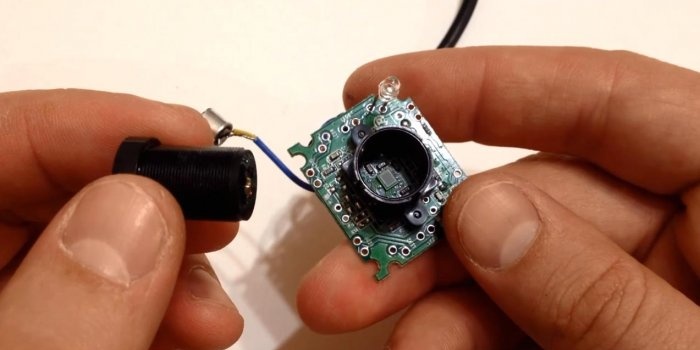
We free the camera from the body by unscrewing the motherboard with the matrix with a screwdriver.
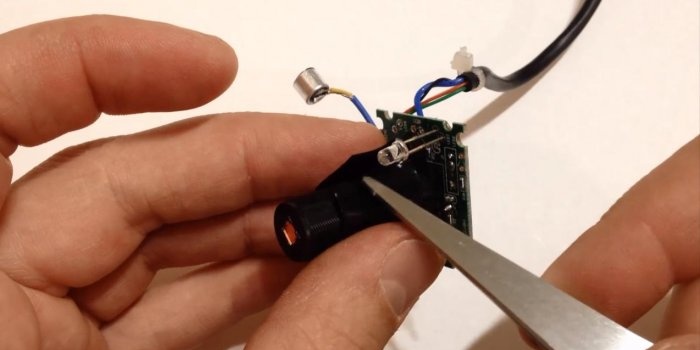
We remove the protective cap and unscrew the lens with lenses and filter. All you need to do is place it in the same place, turning it 180 degrees.
We wrap the junction of the camera lens with the cylindrical body with electrical tape. If desired, it can be additionally glued with a hot glue gun. At this stage, the modified lens can already be tested in action.
We assemble the camera in reverse order, placing its body on the tripod frame with hot glue. The lens should be pointed downwards at the viewing glass of the microscope. The wiring harness can be secured with nylon ties to the tripod stand.
We adapt a low LED flashlight to the sight glass illuminator. It should fit freely under the microscope viewing panel.We connect the camera to the computer, and after a while the image will appear on the monitor screen.
The assembly is ready, it can be checked on any object, for example, by examining the crystal lattice of a pencil lead or the pixel structure of the screen of your smartphone. A popular trend today is the use of such homemade or inexpensive microscopes to control the soldering of small parts on electronic boards. Your child will undoubtedly like it, and perhaps awaken an interest in learning about the world around us.
We all know this device from school. In it we looked at bacteria, living and dead cells, objects and objects that we all see every day. Through a narrow viewing lens, they miraculously turned into models of lattices and membranes, nerve plexuses and blood vessels. At such moments you realize how big and multifaceted this world is.
Recently, microscopes have begun to be made digital. They are much more convenient and efficient, because now you don’t have to look closely at the lens. Just look at the monitor screen, and we see an enlarged digital image of the object in question. Imagine that you can make such a miracle of technology with your own hands from an ordinary webcam. Don't believe me? We invite you to verify this with us.
Necessary resources for making a microscope
Materials:
- Perforated plate, corner and brackets for fastening wooden parts;
- A section of profile pipe 15x15 and 20x20 mm;
- Small fragment of glass;
- Webcam;
- LED flashlight;
- M8 bolt with four nuts;
- Screws, nuts.
Tools:
- Electric drill or screwdriver with a 3-4 mm drill;
- Pliers;
- Phillips screwdriver;
- Hot glue gun.
Assembling a microscope - step-by-step instructions
For the tripod base of the microscope we use perforated plates and metal corners. They are used to join wooden products. They are easily bolted together, and many holes allow this to be done at the required level.
Step one - install the base
We cover the flat perforated plate on the back side with soft furniture pads. We simply glue them on the corners of the rectangle.
The next element will be a bracket or corner with versatile shelves. We fasten the short shelf of the bracket and the base plate with a bolt and nut. We tighten them with pliers for reliability.
We mount two small brackets on the edge of the plate on both sides. We attach two more longer corners to them so that we form a small frame. This will be the base for the microscope viewing glass. It can be made from a small piece of thin glass.
Step two - make a tripod
We make a tripod from a piece of square profile pipe 15x15 mm. Its height should be about 200-250 mm. There is no point in doing more, since exceeding the distance from the viewing glass reduces the quality of the image, and less risks being overexposed and incorrect.
We attach the tripod to a perforated bracket, and on top of it we place a small piece of 20x20 pipe so that it moves freely along this stand.
We make an open frame from two brackets overlapped with each other. We choose longer bolts so that they are enough to tighten this frame around the moving section of the pipe. We place a plate with two holes on the sides on them and secure it with nuts.
To adjust the distance of the frame from the viewing glass, use an M8x100 mm bolt. We will need two nuts to fit the bolt size, and two larger ones. We take epoxy glue and glue the bolt nuts to the tripod in three places. A nut screwed onto the end of a bolt can also be secured with epoxy.
Step three - making the lens
In place of the tube with an eyepiece in our microscope there will be a regular webcam. The higher the resolution, the better; the connection to a computer can be either wired (USB 2.0, 3.0), or via Wi Fi or Bluetooth.
We free the camera from the body by unscrewing the motherboard with the matrix with a screwdriver.
We remove the protective cap and unscrew the lens with lenses and filter. All you need to do is place it in the same place, turning it 180 degrees.
We wrap the junction of the camera lens with the cylindrical body with electrical tape. If desired, it can be additionally glued with a hot glue gun. At this stage, the modified lens can already be tested in action.
Step four - final assembly of the microscope
We assemble the camera in reverse order, placing its body on the tripod frame with hot glue. The lens should be pointed downwards at the viewing glass of the microscope. The wiring harness can be secured with nylon ties to the tripod stand.
We adapt a low LED flashlight to the sight glass illuminator. It should fit freely under the microscope viewing panel.We connect the camera to the computer, and after a while the image will appear on the monitor screen.
The assembly is ready, it can be checked on any object, for example, by examining the crystal lattice of a pencil lead or the pixel structure of the screen of your smartphone. A popular trend today is the use of such homemade or inexpensive microscopes to control the soldering of small parts on electronic boards. Your child will undoubtedly like it, and perhaps awaken an interest in learning about the world around us.
Watch the video
Similar master classes
Particularly interesting
Comments (0)