In what cases is “grounding” used, and in which “grounding”?
Grounding and grounding – ensuring the safety of people working with electrical installations and networks, using household or industrial appliances powered by electricity. Any failure of such devices associated with a violation of insulation threatens the contact of dangerous voltage with exposed conductive parts of the housing.
Effective protection is possible with a clear understanding of the physical meaning and essence of “earth” and “zero” and their correct use in practice.
To eliminate different interpretations of the concepts “zero” and “ground”, you need to refer to established norms and accepted standards. Design, installation and operation are reflected in the main guiding document for the power industry - the Rules for the Construction of Electrical Installations (PUE). Chapter 1.7 of the first section contains complete information about grounding switches, grounding protective conductors, systems and circuits. Section 3 describes protection and automation schemes. The seventh section indicates how networks are equipped, including in public and residential premises.
Protection consists of creating a physical connection between conductive parts of the equipment body, which, if the insulation is damaged, may be exposed to dangerous voltage, with various points in the network:
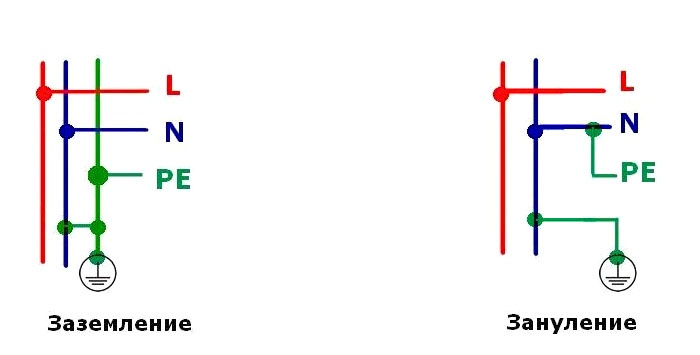
Both connections provide protection. But they implement it in different ways, depending on the connection location.
Electrical installations up to 1000 volts are divided into systems in which the neutral of the energy source is:
A non-industrial consumer is usually powered using a two-wire circuit using two conductors - phase and neutral. All electricity consumers used to be powered according to this scheme, but now it is only permissible for new buildings, to which electricity is supplied via an overhead line.
Modern PUE requirements dictate the conditions for supplying electricity using:
An example would be connecting a residential apartment building to a transformer substation. It is made of a cable with five cores. Inside the building, three phases are distributed through group distribution devices by three wires to single-phase consumers, evenly distributing the load. This is easy to do on new construction, but existing homes already have wiring. It is impossible to immediately remake all of it to meet new requirements, with the construction of grounding conductors.
Many household appliances with three-wire cords and sockets are sold and used, the grounding of which is mandatory. The design features of the standard power systems used will help solve this problem if it is impossible to build a separate grounding loop at the consumer.
In multi-storey buildings of old construction, electricity is supplied according to the TN-C-S scheme, when the neutral on the transformer is solidly grounded, with two wires. It is supplied to the panel or cabinet with a PEN conductor, further distributed among groups and consumers along with phase L.
If you need to turn on, for example, an electric water boiler, you must provide protection. If the heater insulation breaks down, a leak will occur into the housing, which contains water. The water supply network will be under voltage. To prevent this, you need to replace the socket with a three-prong one that matches the plug. From there, lead an additional protective wire of yellow-green coloring into the entrance of the house to the distribution panel.It is bolted to the body of the panel, and in the apartment it is connected to the ground contact of the socket.
It is strictly forbidden to combine the neutral and body contacts directly in the socket.
Effective protection is possible with a clear understanding of the physical meaning and essence of “earth” and “zero” and their correct use in practice.

Terms, definitions
To eliminate different interpretations of the concepts “zero” and “ground”, you need to refer to established norms and accepted standards. Design, installation and operation are reflected in the main guiding document for the power industry - the Rules for the Construction of Electrical Installations (PUE). Chapter 1.7 of the first section contains complete information about grounding switches, grounding protective conductors, systems and circuits. Section 3 describes protection and automation schemes. The seventh section indicates how networks are equipped, including in public and residential premises.
A ground electrode is a circuit artificially made from conductive elements that is in direct contact with the ground.
Neutral is the point where one of the ends of all phase windings of an alternating current source (three-phase generator or substation step-down transformer) is connected together. Under ideal balanced load conditions, the currents of each phase are equal and cancel themselves out. Therefore, such a point has no potential and is called zero.
Protection consists of creating a physical connection between conductive parts of the equipment body, which, if the insulation is damaged, may be exposed to dangerous voltage, with various points in the network:
- Grounding - connecting the wire to the neutral. In the event of an accident, the phase closes to zero, causing the circuit breaker or fuse to trip. A current equal to the phase current flows in the neutral conductor under load. The insulation of this wire is blue.
- Protective grounding is a connection to the grounding circuit that removes dangerous voltage from the housing to the ground. Current flows in the grounding wire only during an accident. It is painted with yellow-green stripes.

Both connections provide protection. But they implement it in different ways, depending on the connection location.
Electricity supply methods
Electrical installations up to 1000 volts are divided into systems in which the neutral of the energy source is:
- solidly grounded, when the neutral wire is deliberately connected to the ground electrode;
- isolated from the ground.
A non-industrial consumer is usually powered using a two-wire circuit using two conductors - phase and neutral. All electricity consumers used to be powered according to this scheme, but now it is only permissible for new buildings, to which electricity is supplied via an overhead line.
Modern PUE requirements dictate the conditions for supplying electricity using:
- 3 wires – phase (L), neutral (N), protective (PE) from the grounding conductor for a single-phase network;
- 5 wires – three phases (L1-L3), N, PE for three-phase power.
An example would be connecting a residential apartment building to a transformer substation. It is made of a cable with five cores. Inside the building, three phases are distributed through group distribution devices by three wires to single-phase consumers, evenly distributing the load. This is easy to do on new construction, but existing homes already have wiring. It is impossible to immediately remake all of it to meet new requirements, with the construction of grounding conductors.
Methods used to organize protection
Many household appliances with three-wire cords and sockets are sold and used, the grounding of which is mandatory. The design features of the standard power systems used will help solve this problem if it is impossible to build a separate grounding loop at the consumer.
In multi-storey buildings of old construction, electricity is supplied according to the TN-C-S scheme, when the neutral on the transformer is solidly grounded, with two wires. It is supplied to the panel or cabinet with a PEN conductor, further distributed among groups and consumers along with phase L.
If you need to turn on, for example, an electric water boiler, you must provide protection. If the heater insulation breaks down, a leak will occur into the housing, which contains water. The water supply network will be under voltage. To prevent this, you need to replace the socket with a three-prong one that matches the plug. From there, lead an additional protective wire of yellow-green coloring into the entrance of the house to the distribution panel.It is bolted to the body of the panel, and in the apartment it is connected to the ground contact of the socket.
It is strictly forbidden to combine the neutral and body contacts directly in the socket.
Watch the video
Similar master classes
Particularly interesting
Comments (5)












