How to connect low-voltage converters in series and get 220 V
Everyone who is interested in electronics is accustomed to the classic type of increasing voltage to the required value: in the form of a single converter with or without a transformer. But there is another alternative way, to obtain any constant voltage with a certain gradation step.
This method is based on the sequential connection of low-voltage converters into a single circuit.
Will need
- Boost converter MT3608 - 8 pcs - http://alii.pub/5uzvqz
- 18650 battery - 8 pcs - http://alii.pub/5becfz
- Box for 18650 batteries - 8 pcs - http://alii.pub/69w5ej
- Wires.
Serial connection of converters
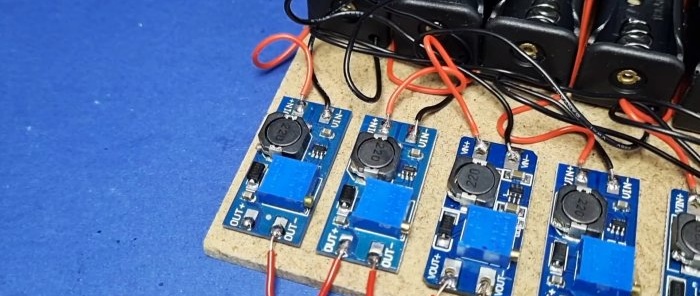
In the example we will use the Chinese MT3608 boost converter.
This module does not have galvanic isolation, so it will not be possible to power all boards from a single source. We connect the module to the box and install the battery. We unscrew the variable resistor slider to the maximum. We measure the output voltage.
Almost as stated - 28 V with a slight excess.The maximum load according to the passport is 2 A, naturally this is a Chinese exaggeration, or simply a peak value.
As a result, through simple calculations, the value was revealed: to obtain a voltage of 220-240 V, you need 8 converter boards and the same number of batteries.
We take a base from any material and glue the boxes in a row using hot glue.
We connect the outputs from each box to its own module, which we also glue with hot glue.
We connect the outputs of the converters in series. That's all.
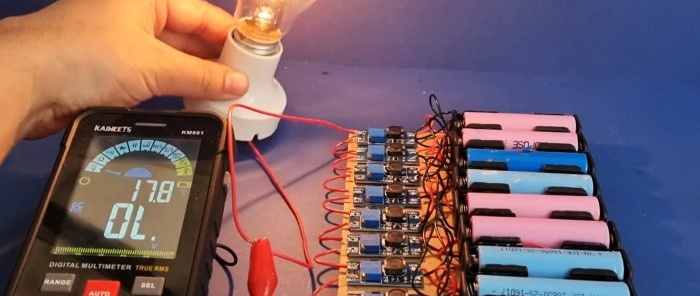
The test will be connecting a 220 V incandescent lamp.
The result was a very large voltage drop. But if you connect an LED or energy-saving lamp, the voltage does not drop.
Who needs it and what are the pros and cons
For quickly obtaining constant voltage, this is an excellent option. The device can be adjusted in 28 V steps, which can be useful.
The only downside that can be noted is that the converted voltage is constant, although in some places this can also serve as a plus.