How to make a 220 V Power Bank
This portable charger (Power Bank), unlike all manufactured models, produces not only 5 V DC, but 220 V AC, which is very advantageous and can be used in a wider range. Power is 60 W, which is quite a lot for such a small box that easily fits in your pocket.
Even a beginner without proper knowledge of electronics can assemble this power bank, since everything is built on ready-made Chinese modules.
Will need
- Li-ion 18650 batteries - 3 pcs.
- Holder (case) for 18650 batteries.
- DC-DC converter, 12V to 5V USB.
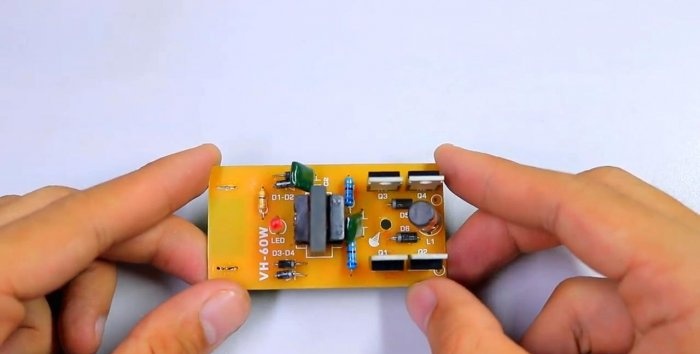
- DC-AC converter, from 12 V to 220 V 60 W.
- Toggle button.
Other: plastic for making the case, hot and second glue.
On Ali Express you can find batteries of various capacities from 600 mA*H to 9800 mA*H, at a voltage of 3.7 V. The total capacity of the power bank is made up of the sum of the capacities of all elements. That is, if all three batteries have a capacity of 3000 mA*H, then the capacity of the power bank will be 9000 mA*H.
The case must be selected for three elements.
Regarding the boost converter (inverter), I want to answer: the power of the presented specimen is 60 W.But you are unlikely to find exactly this one. There will likely be other smaller converter boards available to you. In terms of power, they predominate at either 40 W or 150 W. You can take any.
A distinctive feature of such mini inverters is that they practically do not consume energy in idle mode. They also have a very high efficiency, so the entire capacity will be used in full.
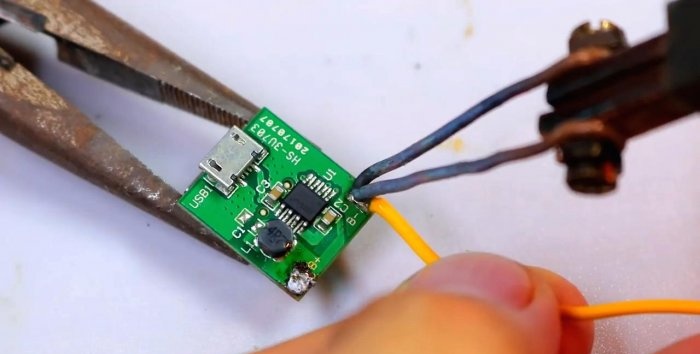
5V buck converter board with USB socket. It is necessary to directly charge devices from 5 V via USB.
Manufacturing Power Bank for 220 V
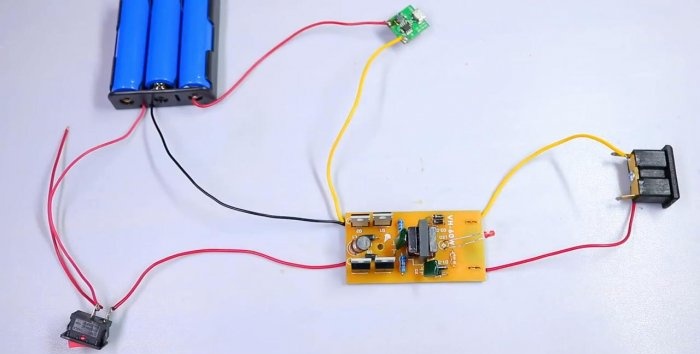
We install the elements in the holder and measure the total voltage. In the case they are connected in series and the output voltage of fully infected batteries totals approximately 12.5 V.
We solder a toggle switch in series with the elements, which will break the entire circuit and more than one converter will not just waste capacity after turning off.
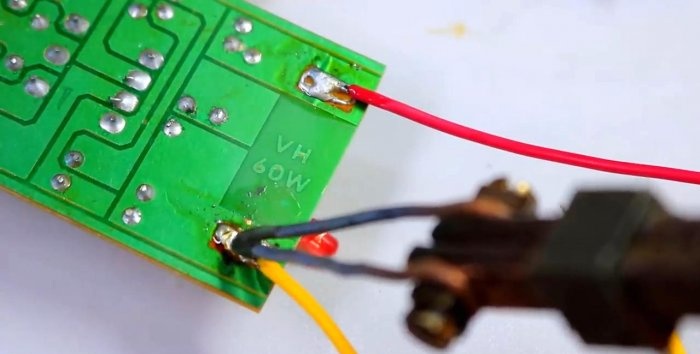
We solder the wires to the 220 V converter inputs.
And at 5 V.
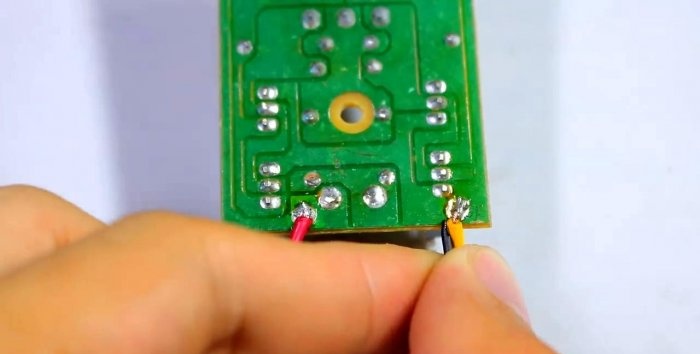
Solder the wires to the 220 V output.
Let's prepare a universal power outlet.
Something like this. You don’t need to go into too much detail, since the connection is not entirely clear, but it works. The 5V converter was soldered directly to the block, but was then soldered in parallel to the inverter.
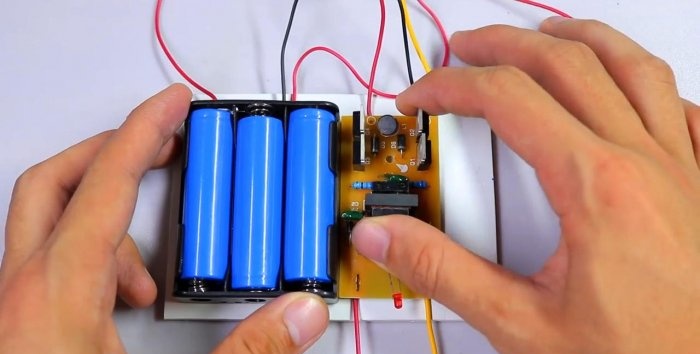
Let's start making the device body. For these purposes, it is good to use thick PVC plastic, foam board, etc. We arrange the elements and roughly cut out a rectangle.
Place the case with the elements on hot glue.
The same goes for the inverter board.
This was the bottom. We cut the top to the same dimensions. We make grooves for the switch and socket.
In the center you can notice a hole - this is under Light-emitting diode, which is located on the inverter board and sticks out on the legs.
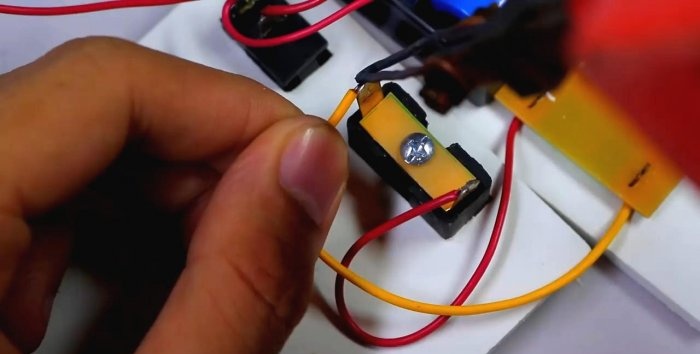
Solder the wires to the socket.
In the side wall we attach a 5 V step-down converter with a USB socket and an output connector, which we solder parallel to the entire 12.5 V battery.
This connector will be used to recharge the cookbank.
We assemble the body, gluing all the parts with second glue.
View of a completely finished device.
Power bank test
We turn the switch to the on position and measure the output voltage at the 220 V socket. It shows 203, but this is not critical in allowing for discrepancies.
We plug in a 60 W light bulb, testing it for maximum load capacity. The lamp is on.
We try to charge the mobile phone through the charger. Charging is in progress.
We try to work and charge the laptop battery. Everything works without problems.
We try to charge directly via USB.
Everything works as it should!
Charger
The device is charged via a 12 V adapter plugged into the connector.
This is not entirely correct, as it turns out. Batteries of this type must be charged through a special board 3S BMS boards. Thanks to the use of such a board, there will be no voltage discrepancy between elements in the same circuit.
That's all! Now you will have a 220 V socket in your pocket!
I would like to finally note that the 220 V output has a high frequency of about 800 Hz. Such a device cannot power asynchronous motors, transformers and other equipment that requires an exact frequency of 50 Hz. And for powering switching power supplies for laptops, TVs, chargers, it is quite acceptable.
Watch the video
Similar master classes
Particularly interesting
Comments (6)