The most reliable relay for turn signals
As you know, all modern cars are equipped with direction indicators, which are a flashing light on the left or right side of the body or Light-emitting diode. Sometimes a standard electromechanical relay fails, and getting a powerful automotive relay is not always so easy. Semiconductor devices come to the rescue - after all, building such a relay is powerful with just a couple of transistors.
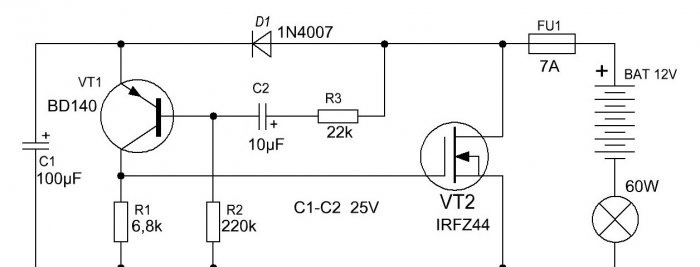
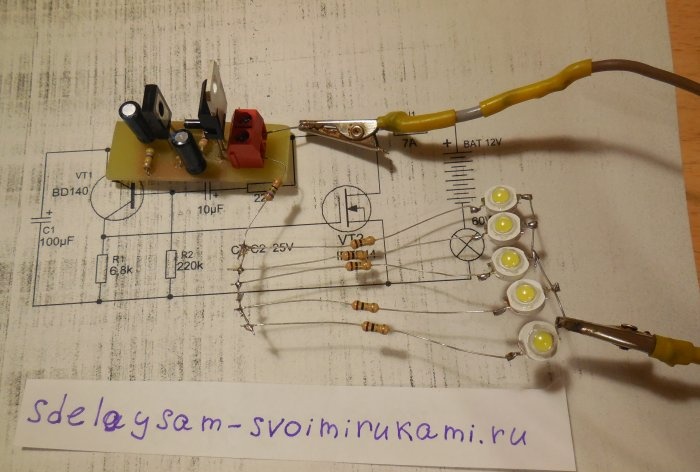
Relay circuit
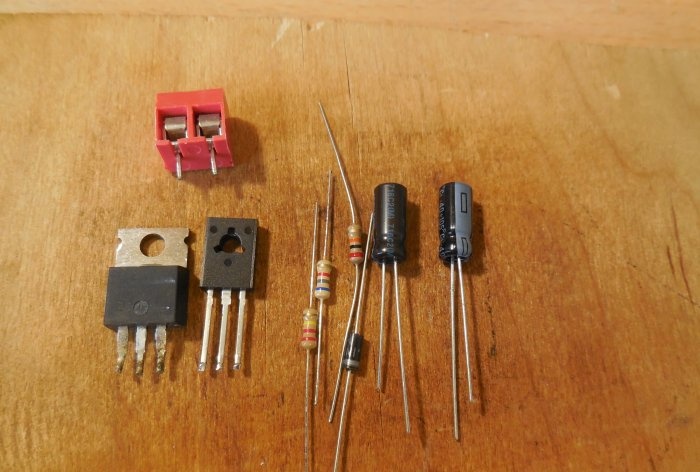
The circuit is an asymmetrical multivibrator; it is connected in an open circuit in series with the light bulb and the power source. When voltage is applied, the light immediately begins to blink. VT2 in the diagram is a field-effect transistor; it is through it that the entire light bulb current flows. It is preferable to use a transistor with the lowest possible open junction resistance. IRFZ44N, IRF740, IRF630 are suitable here. If you use it instead of a light bulb Light-emitting diode low power, you can use a bipolar transistor, for example, TIP122. Transistor VT1 of medium power p-n-p structure, BD140, KT814 are suitable. Diode D1 can be installed 1N4007 or 1N4148. The blinking frequency directly depends on the capacitance of the capacitors and the resistance of the resistors.To increase the frequency, you need to reduce the capacitance of capacitor C2, and to decrease the frequency, on the contrary, increase its capacitance. You can also experiment with the values of other circuit elements and observe how the duty cycle of the pulses changes.
Circuit assembly
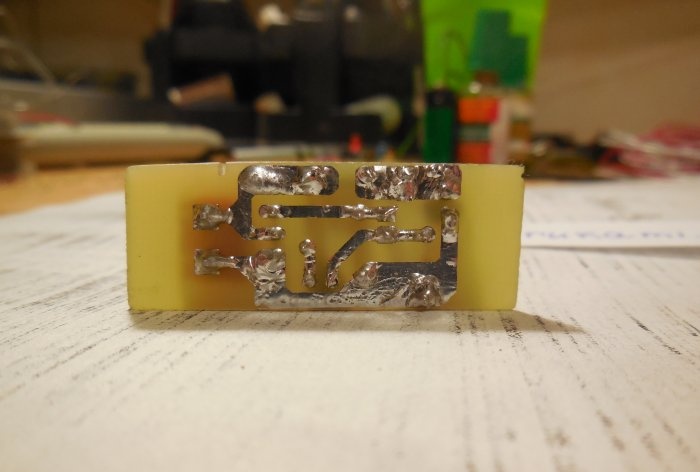
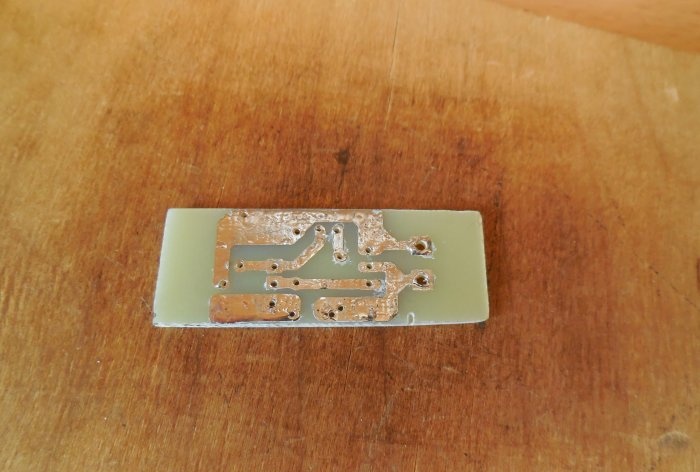
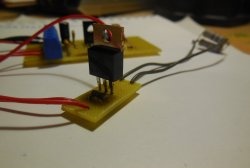
The entire circuit is assembled on a miniature printed circuit board measuring 35 x 20 mm; it can be manufactured using the LUT method. The tracks must be tinned after etching, then the copper will not oxidize.
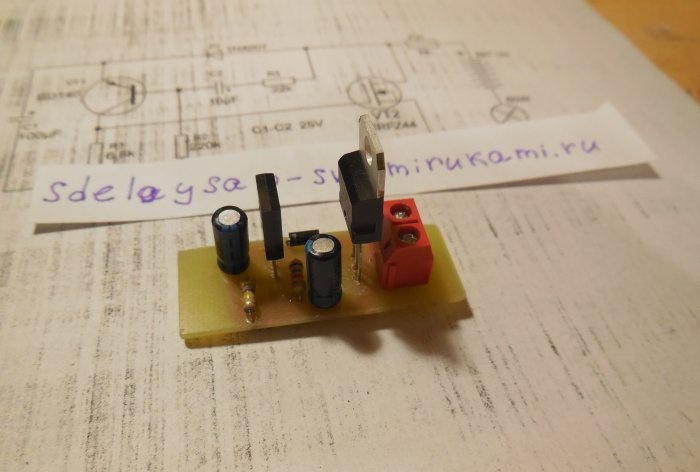
First of all, resistors and a diode are soldered onto the board. After them, everything else is a pair of transistors, electrolytic capacitors and a terminal block. It is important not to confuse the pinout of the transistors and the polarity of the capacitors, otherwise the circuit will not work. When all the parts are soldered onto the board, be sure to wash off the remaining flux and check the correct installation.
Setting up and testing turn signal relays
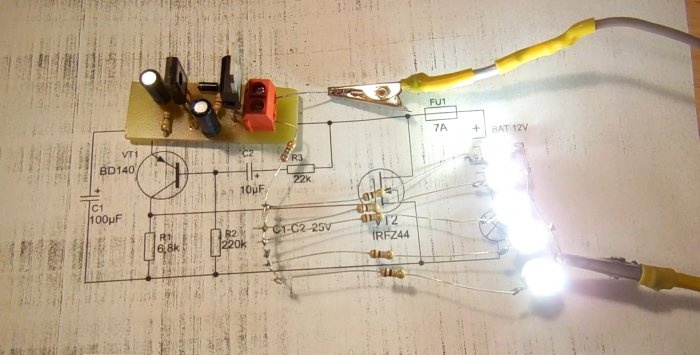
For testing, you can connect several powerful ones as a load. LEDs. We connect the negative of the load directly to the negative of the power supply, and connect the positive to the board. If a light bulb is used for testing, it can be connected with any polarity. We apply voltage and the light immediately begins to blink. The blinking frequency can be changed within a wide range, which is why this circuit can be found in many other applications besides being used as a turn signal relay. For example, you can use it to make a rear flashing light for a bicycle; you just need to increase the flash frequency by decreasing the capacitor capacity. The circuit can switch high power - up to several hundred watts, if you use a field-effect transistor designed for the appropriate current.With a power of more than 100 watts, it is advisable to install the transistor on a small radiator, otherwise it may heat up during long-term operation. This circuit, unlike a traditional electromechanical relay, has no moving parts, so it is much more durable if used with parts of the proper quality. If necessary, a fuse, indicated in the diagram as FU1, is also connected in series with the load. Happy assembly.
Watch the video
The video clearly demonstrates the operation of this circuit; several LEDs with resistors.