Removing Rust with Baking Soda
This is my favorite method for removing rust from heavily corroded metal products. The method is very simple and highly effective. With a little patience, you will get impressive results.
Use this method only outdoors as the process releases highly toxic gases.
What do we need
- 1. Baking soda (I used 400 g per 10 liters of water, but you can try experimenting with the concentration).
- 2. Plastic bucket (must be plastic as a non-conductive material).
- 3. DC 12V power supply.
- 4. Sacrificial metal to which rust will be transferred.
- 5. Copper wires.
- 6. Water.
Preparation
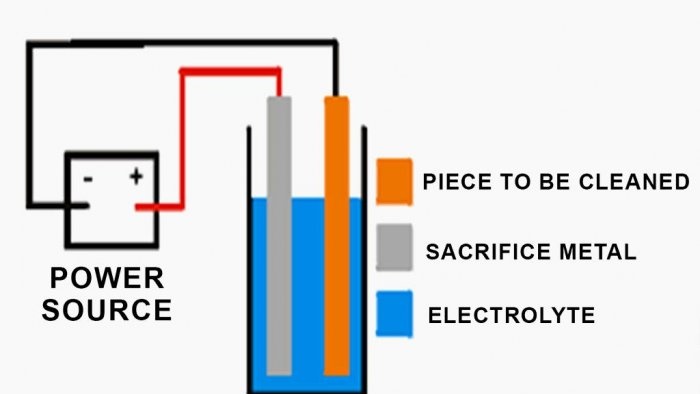
Connect the negative wires from the power source to the parts being restored.
Using copper wires, attach the parts to be cleaned to the black contacts of the power supply, and the sacrificial metal to which the rust is transferred to the yellow contacts (+12 V).
Fill a bucket with water and place metal in it to transfer the rust. Make sure that the fastenings are secure to avoid short circuits. Add baking soda and mix well.
Then lower the parts to be cleaned, avoiding their contact with metal to avoid a short circuit. Double check that you have done everything correctly and start the power supply (see last image). If all steps are performed correctly, bubbles will appear on the surface after a while.
Electrolysis with soda
Purification occurs by electrolysis. A mixture of baking soda and water is an electrolyte that, using an electric current, produces a chemical reaction to separate materials at the electrodes.
The main components of the electrolysis process are:
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity using ions.
DC power supply - provides the energy needed to create or discharge ions in the electrolyte. Electric current is carried by electrons in an external circuit.
The two electrodes are conductors that provide a physical connection between the power source and the electrolyte.
Result of rust removal
I ran the process for two hours, but it should take about six hours to get a good result.
The result depends on the duration of the process. If you are not satisfied with the result, you can repeat the process several times. You can also experiment with the concentration of soda and the current strength in the region of 10 amperes (the process will not start at a current strength of 5 amperes, and at a value of more than 15 amperes, the electrolyte will begin to boil).
After finishing the process, you can clean your products with water and a brush.
Watch the video
Similar master classes
Particularly interesting
Comments (7)