How to power a cooler for cooling an LED matrix at 220 V
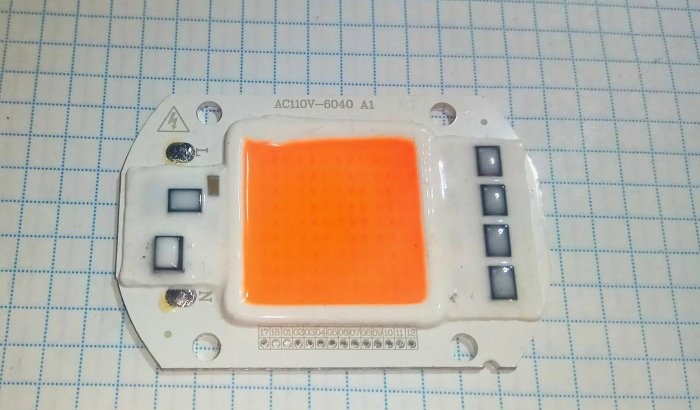
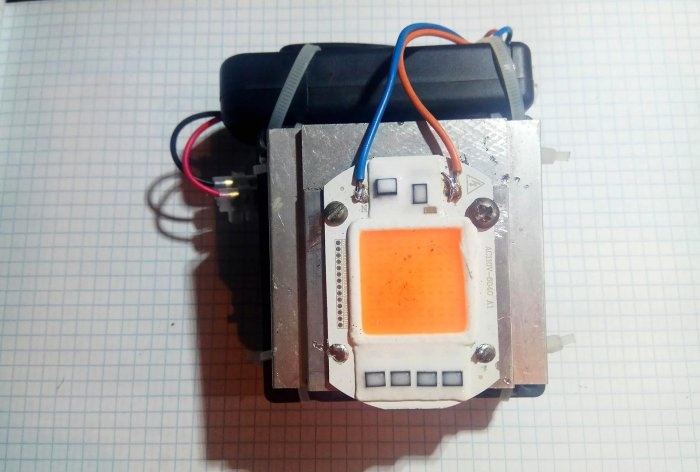
The phyto LED matrix for illuminating plants, having its own power driver, is connected directly to the 220 V network. It works for almost half a day every day, while its body gets very hot. The matrix, attached to an aluminum radiator, receives the necessary cooling from the computer cooler. Constant 12 V for it is obtained from a network adapter, which is not always at hand.
A power supply without a mains transformer is easy to make with your own hands. You will need some radio components and a soldering iron.
The transformer circuit is bulky and heavy. To lower the voltage, use the property of a capacitor to provide reactance to alternating current. If you use a divider with active resistance, problems arise:
1. With large resistor values, the circuit current is small, and the potential difference at the output is insufficient to power the device.
2. Reducing the resistance will increase the voltage, but the current through the quenching resistor will increase, it will heat up intensely until it burns out or starts a fire.
On a capacitor, alternating current and voltage are shifted in phase. At the beginning of the charge cycle, the current is large, and the voltage across the capacitor is small and gradually increases. When the capacitance is charged, the voltage increases and the current drops to zero. At the same time they are not big. The capacitor releases little power and the housing heats up little.
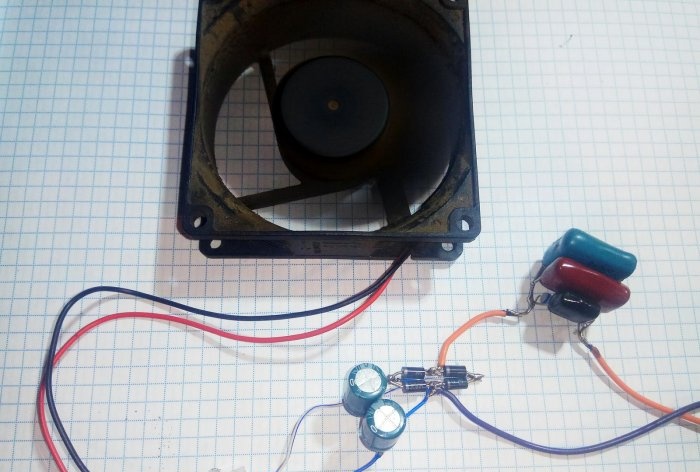
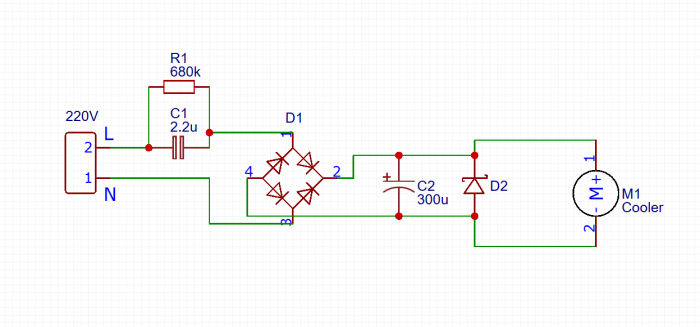
The mains voltage is supplied to the diode bridge through a capacitor. A divider is formed from the reactance of the capacitor and diodes. A small part of the voltage rectified by the bridge is smoothed by an electrolytic capacitor. The 12 V power supply normalized by the zener diode is supplied to the electric motor. A resistor is connected in parallel to the ballast capacitor, smoothing out the current surge when power is applied and ensuring the discharge of the capacitor when turned off.
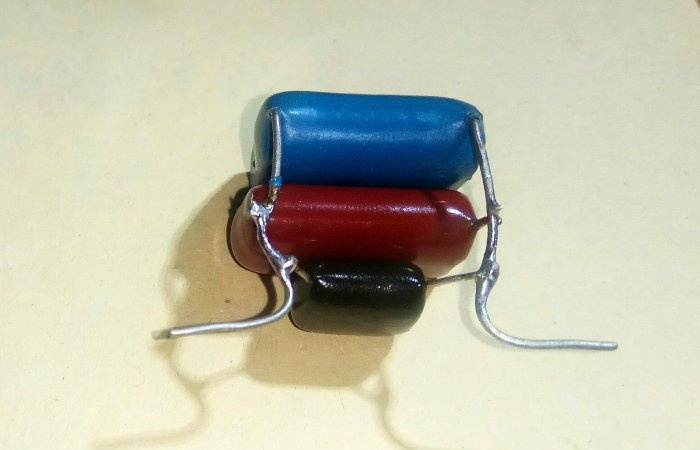
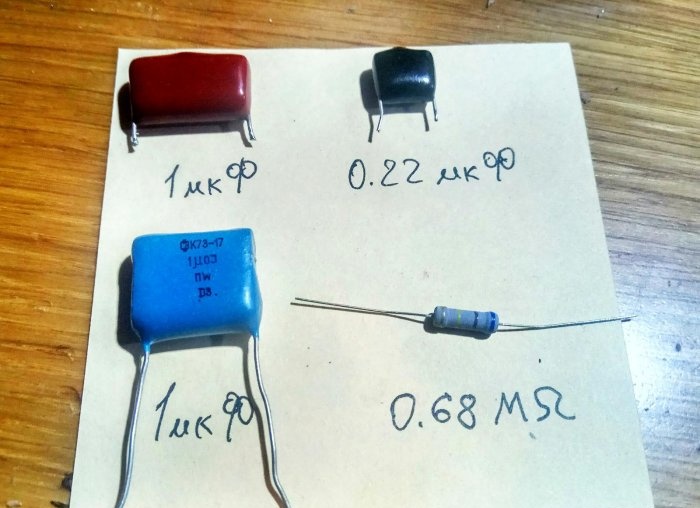
The circuit operates under a mains voltage of 220 V, so capacitors with an operating voltage of at least 600 V, paper type KGB or film K73-17, are used. The thermal dissipation power of the resistor is 0.25÷0.5 W.
The minimum permissible reverse voltage of diodes is 400 V. D226B, KD105B-G or their imported analogues are suitable. The diodes are replaced by a bridge assembly KTs402-407. The zener diode is selected with a maximum current at an operating voltage of 12 V.
Parallel connection of capacitors increases the total capacitance, summing up the ratings of all elements. The desired value is selected by combining several elements.
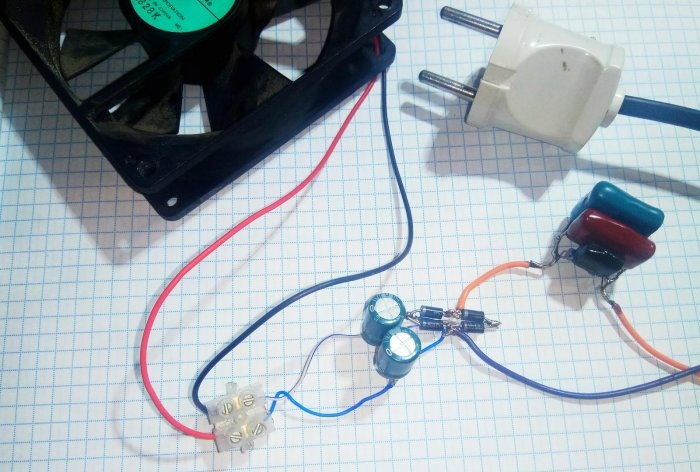
There are few details, but their conclusions are harsh. It is possible to assemble a power supply by surface mounting without a printed circuit board, without short-circuiting the connections of the parts' pins.
The circuit, assembled without installation errors from serviceable parts, starts the cooler engine when the power is turned on.
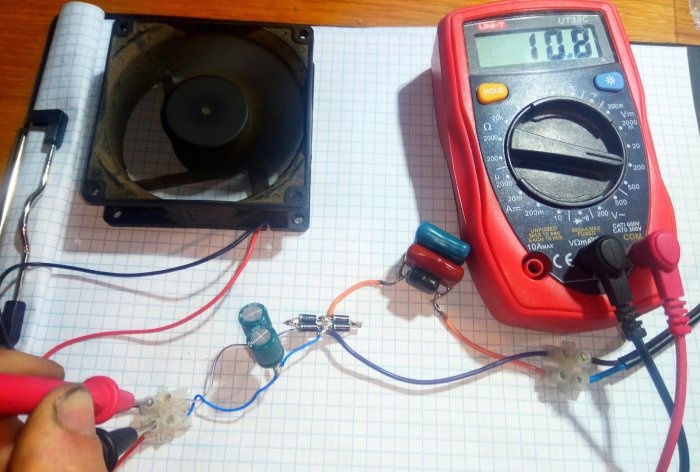
It will help to check the operating parameters multimeter in constant voltage measurement mode, connected in parallel to the cooler. The operating voltage range of the motor is within 9÷14 volts. At the upper limits, the fan noise increases noticeably. Increasing the ballast capacitance increases the output voltage. Reducing is the opposite.
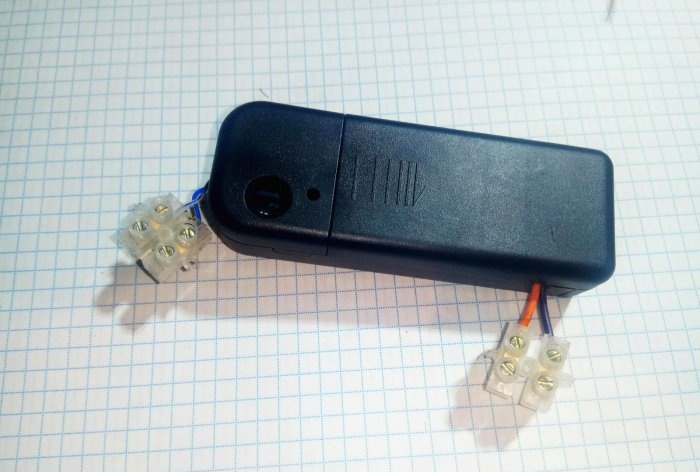
Placing the installation in a plastic case will protect against electric shock. To connect wires, terminal pairs are installed at the input and output of the block.
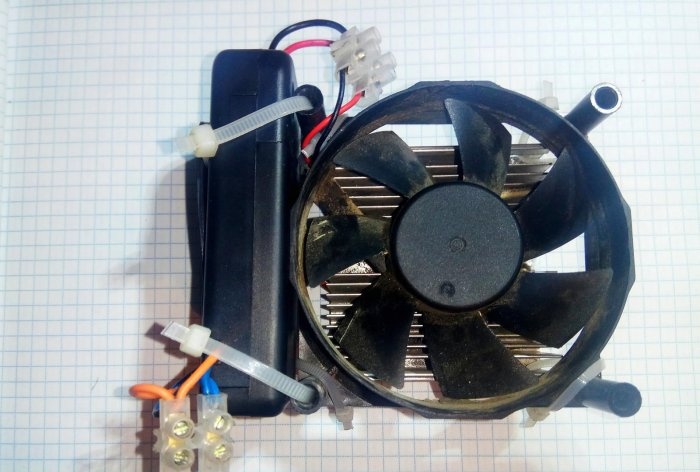
The housing is mounted on a radiator with an LED matrix placed on it. The power cord is connected to the parallel-connected power pins of the LED driver and power supply.
You need to make sure that nothing interferes with the free rotation of the blades.
All circuit elements are under life-threatening 220 V mains voltage, therefore:
The lack of galvanic isolation of the power supply from the network is compensated by its small size, weight and low noise level during operation.
A power supply without a mains transformer is easy to make with your own hands. You will need some radio components and a soldering iron.
Description of the block operation
The transformer circuit is bulky and heavy. To lower the voltage, use the property of a capacitor to provide reactance to alternating current. If you use a divider with active resistance, problems arise:
1. With large resistor values, the circuit current is small, and the potential difference at the output is insufficient to power the device.
2. Reducing the resistance will increase the voltage, but the current through the quenching resistor will increase, it will heat up intensely until it burns out or starts a fire.
On a capacitor, alternating current and voltage are shifted in phase. At the beginning of the charge cycle, the current is large, and the voltage across the capacitor is small and gradually increases. When the capacitance is charged, the voltage increases and the current drops to zero. At the same time they are not big. The capacitor releases little power and the housing heats up little.
The mains voltage is supplied to the diode bridge through a capacitor. A divider is formed from the reactance of the capacitor and diodes. A small part of the voltage rectified by the bridge is smoothed by an electrolytic capacitor. The 12 V power supply normalized by the zener diode is supplied to the electric motor. A resistor is connected in parallel to the ballast capacitor, smoothing out the current surge when power is applied and ensuring the discharge of the capacitor when turned off.
Details
The circuit operates under a mains voltage of 220 V, so capacitors with an operating voltage of at least 600 V, paper type KGB or film K73-17, are used. The thermal dissipation power of the resistor is 0.25÷0.5 W.
The minimum permissible reverse voltage of diodes is 400 V. D226B, KD105B-G or their imported analogues are suitable. The diodes are replaced by a bridge assembly KTs402-407. The zener diode is selected with a maximum current at an operating voltage of 12 V.
Parallel connection of capacitors increases the total capacitance, summing up the ratings of all elements. The desired value is selected by combining several elements.
Installation
There are few details, but their conclusions are harsh. It is possible to assemble a power supply by surface mounting without a printed circuit board, without short-circuiting the connections of the parts' pins.
The circuit, assembled without installation errors from serviceable parts, starts the cooler engine when the power is turned on.
It will help to check the operating parameters multimeter in constant voltage measurement mode, connected in parallel to the cooler. The operating voltage range of the motor is within 9÷14 volts. At the upper limits, the fan noise increases noticeably. Increasing the ballast capacitance increases the output voltage. Reducing is the opposite.
Placing the installation in a plastic case will protect against electric shock. To connect wires, terminal pairs are installed at the input and output of the block.
The housing is mounted on a radiator with an LED matrix placed on it. The power cord is connected to the parallel-connected power pins of the LED driver and power supply.
You need to make sure that nothing interferes with the free rotation of the blades.
Features of the scheme
All circuit elements are under life-threatening 220 V mains voltage, therefore:
- Perform work with the circuit with the power turned off and the ballast capacitor discharged;
- disconnecting the load (cooler) without first turning off the power will lead to failure of the unit;
- It is necessary to protect the circuit from short circuit by installing a fuse.
The lack of galvanic isolation of the power supply from the network is compensated by its small size, weight and low noise level during operation.
Similar master classes
Particularly interesting

Cable antenna for digital TV in 5 minutes

A selection of simple and effective schemes.

Three-phase voltage from single-phase in 5 minutes

Starting a three-phase motor from a single-phase network without a capacitor

Eternal flashlight without batteries

How to make an inexpensive but very powerful LED lamp
Comments (7)